Power point questions | Nursing homework help
This is a Collaborative Learning Community (CLC) assignment.
Nursing theories are tested and systematic ways to implement nursing practice. Select a nursing theory and its conceptual model. Prepare a 10‐15 slide PowerPoint in which you describe the nursing theory and its conceptual model and demonstrate its application in nursing practice. Include the following:
- Present an overview of the nursing theory. Provide evidence that demonstrates support for the model’s efficacy in nursing practice. Explain how the theory proves the conceptual model.
- Explain how the nursing theory incorporates the four metaparadigm concepts.
- Provide three evidence‐based examples that demonstrate how the nursing theory supports nursing practice. Provide support and rationale for each.
Refer to the resource, “Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations,” located in the Student Success Center, for additional guidance on completing this assignment in the appropriate style.
While APA style is not required for the body of this assignment, solid academic writing is expected, and documentation of sources should be presented using APA formatting guidelines, which can be found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Refer to the LopesWrite Technical Support articles for assistance.
Questions:
1. Explain how the nursing theory incorporates the four metaparadigm concepts.
2. Provide three evidence-based examples that demonstrate how the nursing theory supports nursing practice. Provide support and rationale for each.
The theory that my group choose was:
Hildegard Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations Theory
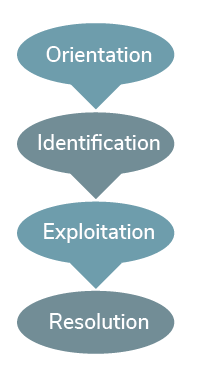
Hildegard Peplau’s interpersonal relations theory is referred to as psychodynamic nursing, which refers to the understanding of one’s behavior. Peplau’s (1909-1999) work was a major contribution to mental health laws and defined nursing as an interpersonal process of therapeutic interactions between an ill individual in need of health services and an educated nurse trained to recognize and respond to those needs (Peplau, 1952). She considered the person to be an organism that desires to reduce tension or anxiety. The environment is not clearly defined but is made up of existing forces outside of the person. Health is defined as forward movement of the human process toward creative and productive community living. Nursing is a therapeutic interpersonal process existing in four phases: orientation, identification, exploitation, and resolution (see Figure 2.5).
The nurse has a variety of roles that include stranger, teacher, resource, counselor, technical expert, and leader (Creasia & Friberg, 2011). This theory can be explained as the understanding of the interpersonal relationship between the patient and the nurse. Peplau recognized that such a relationship does exist, and the nurse is not just a messenger between the physician and patient.
Figure 2.5
Hildegard Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations Theory
Lecture:
Nursing Theory
A theory is a collection of statements that explain a relationship between two or more ideas. Theory maintains a central role in the evolution of the nursing discipline. It is something all nurses use in their daily practices, whether known or not. Relatively new, nursing theory is a structure of purposeful and systematic ideas that help to organize disciplinary thinking and influence practice. Much discussion and debate have occurred regarding the various theory definitions. Levine (1995) promoted acceptance of nursing theory, which she called the intellectual life of nursing. She identified that students often fail to embrace nursing theory and do not fully grasp the importance of nursing theory and its relevance for practice and education.
Understanding nursing theory strengthens the focus of care by guiding nursing practice. It may help to think about nursing theories as various lenses used to view different perspectives of known nursing phenomena. For example, Dorothy Orem’s self-care deficit theory focuses on assisting others in managing self-care to maintain or improve human function at an effective level (Orem, 1995). Also, Sister Callista Roy’s adaptation theory explains how individuals are in constant interaction with a changing environment and that the individual must adapt to change to have a positive response (Creasia & Friberg, 2011).
Example of Dorothy Orem’s Self-Care Deficit TheoryAn elderly man recently received a total hip replacement. During the discharge process, the registered professional nurse educates the patient about many things, including activity restrictions, medications, and wound care. The nurse also reviews activities of daily living, such as showering and toileting. The nurse realizes that the patient’s balance may be altered and discusses fall precautions with the patient. Detailed discharge instructions are an example of moving the patient from a state of dependence on others for care to a state of independence and self-care.Example of Sister Callista Roy’s Adaptation TheoryThe school nurse receives a phone call from a parent of an eighth-grade female student stating that the student recently suffered a femoral fracture from a trampoline injury that required open reduction internal fixation. She has successfully recovered to the point that she can return to class next week. The nurse realizes that because of the full-leg cast the student will be excused from physical education class and likely will require assistance with mobilization and toileting. Based on the student’s age, psychosocial issues are likely to be involved due to an altered self-concept related to body image. Her balance may be altered as well. Ultimately, the student demonstrated a positive attitude and adapted well to this life-altering event.Nursing theory is present in day-to-day interactions with patients. The core values derived from theoretical assumptions can serve as a foundation upon which to build practices. The goal of applying theory is to improve practice.
The nursing profession is an art and science involving a complex mix of many parts. Nurses are expected to perform the science of nursing through medical and technical competencies, such as nursing skills, academic knowledge, and professional performance. Nurses must become lifelong learners and engage in continuing education throughout their careers to maintain those nursing skills and competencies. Included in the science of nursing are theories, conceptual models, and research that is specific to nursing. The art of nursing requires a foundation of nursing skills, academic knowledge, and professional performance. It is difficult to define or measure the art of nursing other than by looking at the pronounced noticeability of its absence. Treating patients with dignity and respect, being cognizant of nonverbal cues, and using active listening and communication skills are all qualities patients and families value highly. Nurses should strive to find a balance between the science and the art of nursing in their practices (Palos, 2014).
Nursing is a knowledge-based discipline and profession that incorporates a body of knowledge to guide its practice (Smith & Parker, 2015). Because nursing is a profession, nurses are required to meet specific educational qualifications. Education is systematically obtained from colleges and universities that ultimately produce knowledge-based professional nurses who can practice autonomously. The following characteristics define the meaning of a professional (Creasia & Friberg, 2011):
- Formal education required
- Lifelong mission, recognized as life work
- Encompass knowledge
- Service to society
- Practice autonomously
- Practice guided by ethics
- Professional culture and values
- Compensation received
Metaparadigm
Theories are built upon a foundation of concepts. Theoretical statements compose a theory. The concepts incorporated into theoretical statements include areas of interest to the discipline. For nursing theory, these concepts include person, environment, health, and nursing, also referred to as metaparadigm. The metaparadigm includes basic assumptions regarding the theory and highlights areas vital to the nursing discipline and ultimately patient care (see Figure 2.3).
Figure 2.3
Metaparadigm of Nursing Concepts
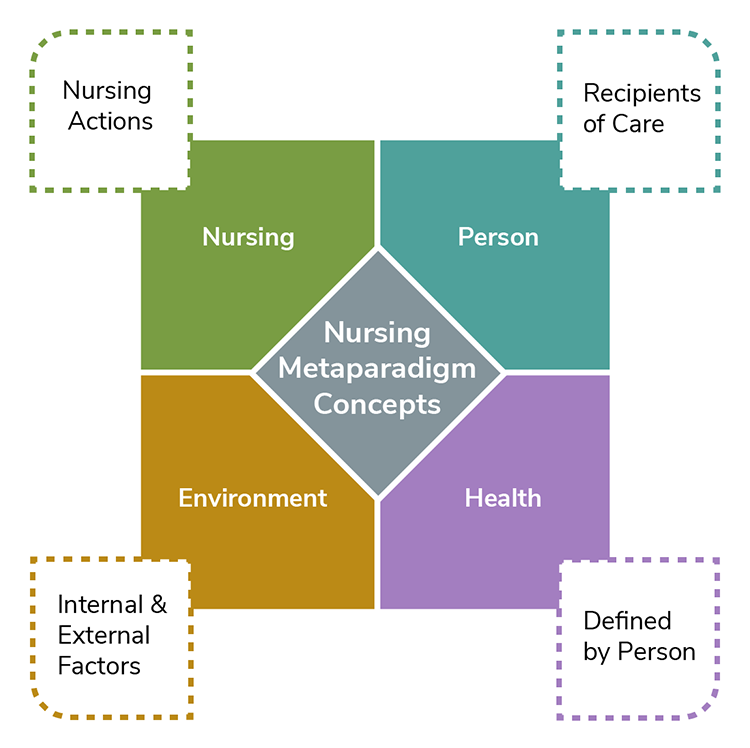
Note. Adapted from “Nursing Metaparadigm Concepts,” by CJT Consulting & Education, 2017.
Person refers to the patient, client, individual, family, community, or group. These are the recipient(s) of said nursing care. Environment includes external and internal space associated with the person. Health encompasses all areas of, or lack of, the person(s) wellbeing. As the final metaparadigm component, nursing expresses the goal of nursing that is specific to the theory (McEwen, 2007).
Conceptual Models
Theories can be categorized according to their complexity. These categories include practice theories, midrange theories, and grand theories (also referred to as conceptual models). Conceptual models explain a particular way of thinking, or a mental picture of how the theory fits together, according to the theorist. A conceptual model is the organizing structure that defines the theory.
Types of Theories
Nursing theories are categorized by their level of complexity and are identified as practice theories, midrange theories, or grand theories.
Practice Theory
The purpose of nursing theory is to improve nursing practice, and the lives of patients, families, and communities served by nursing practice. Practice theory defines the delivery of nursing care in specific situations related to practice, incorporating “nurses’ clinical wisdom” (McEwen, 2007) by answering clinical questions. Practice theory is limited in scope in that it focuses on specific areas of nursing, such as a specific patient population or a certain type of nursing practice. Nursing interventions and actions in response to patient-specific needs are often prescribed. Practice theory offers a specific framing of how nurses handle situations within their scope of practice (Levine, 1995). Scenarios of practice theories are often reviewed in nursing journals that focus on management of disease or journals that discuss nursing interventions related to specific patient populations (Creasia & Friberg, 2011).
General System Theory
General system theory is a broad theory that specifies any system being studied as composed of smaller subsystems and also a part of a larger subsystem. It suggests that a system is a set of interrelated parts that are constantly interacting with the environment to attain a common goal (Creasia & Friberg, 2011). In other words, a system is more than the sum of its parts (Boettcher, 1996). When studying the circulatory system, for example, one cannot simply study the components of blood, but must also include the cardiovascular system, the vascular system, respiratory system, and so on to understand how the circulatory system functions.
Change Theory
Change theory is one of the most commonly used theories related to nursing education and patient learning. This theory’s governing principle is that by using certain motivating factors, patients feel empowered and desire to change unhealthy habits. By setting goals and offering incentives, learning and change occur for the patient.
Kurt Lewin (1890-1947), commonly referred to as the father of psychology, was known for his life space or field theory. Kurt Lewin’s field theory states that human behavior is related to both the individual and the environment. Lewin explored human behavior by performing field research. The concepts of driving forces, restraining forces, and equilibrium were used by Lewin to explain human behavior (McEwen, 2007). Lewin believed that desired change in human behavior could occur by first identifying the undesired behavior, then understanding the cause of such behavior, and what forces would need to be strengthened or weakened to bring about change (Burnes & Cooke, 2013). This theory can be applied to many areas of nursing, including mental health, or any area that desires improved health outcomes based on patient compliance with prescribed regimens.
Coping/Adaptation Theory
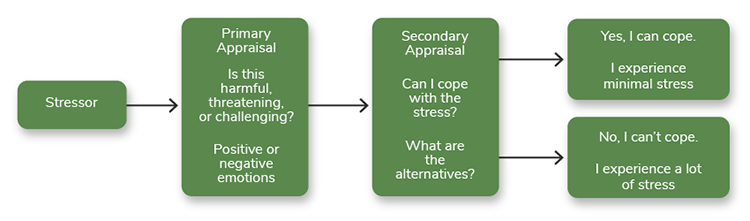
The ability to cope requires the body to adapt continually to a changing environment. Richard Lazarus (1922-2002) was a psychologist and author who was best known for his theoretical work related to coping. Developed in 1984, Richard Lazarus’s theory of stress, coping, and adaptation centers on how an individual copes with stressful situations (see Figure 2.4).
The theory focuses on various psychological responses to stress that are considered negative, such as emotional distress, anxiety, depression, anger, and fear, to name a few. Lazarus saw these responses as coping mechanisms. Stress is viewed as more than a stimulus causing a response. Nurses can apply this theory to assess the effects of stress on the individual patient. Physical and psychological responses to stressors can occur (Smith & Parker, 2015). For example, an individual working in a stressful environment may develop emotional distress that causes disruptive outbursts and chronic overeating. Physical responses may include high blood pressure and obesity. Another example would be soldiers returning to civilian life and experiencing post-traumatic stress disorder.
Figure 2.4
Richard Lazarus’s Theory of Stress, Coping, and Adaptation
Midrange Theory
Midrange theories are not as complicated as grand theories. Midrange theories contain fewer concepts, are easier to use, and usually contain single applications that can be applied to a variety of practice settings.
Hildegard Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations Theory
Hildegard Peplau’s interpersonal relations theory is referred to as psychodynamic nursing, which refers to the understanding of one’s behavior. Peplau’s (1909-1999) work was a major contribution to mental health laws and defined nursing as an interpersonal process of therapeutic interactions between an ill individual in need of health services and an educated nurse trained to recognize and respond to those needs (Peplau, 1952). She considered the person to be an organism that desires to reduce tension or anxiety. The environment is not clearly defined but is made up of existing forces outside of the person. Health is defined as forward movement of the human process toward creative and productive community living. Nursing is a therapeutic interpersonal process existing in four phases: orientation, identification, exploitation, and resolution (see Figure 2.5).
The nurse has a variety of roles that include stranger, teacher, resource, counselor, technical expert, and leader (Creasia & Friberg, 2011). This theory can be explained as the understanding of the interpersonal relationship between the patient and the nurse. Peplau recognized that such a relationship does exist, and the nurse is not just a messenger between the physician and patient.
Figure 2.5
Hildegard Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations Theory

Note. Adapted from “Developmental States of the Nurse-Client Relationship: Peplau’s Interpersonal Relations Theory,” from Effective Communication in Nursing: Theory and Best Practice, by Southeastern University.
Imogene King’s Theory of Goal Attainment
The central concept of Imogene King’s theory of goal attainment is that personal, interpersonal, and social systems all interact together to reach a common goal (see Figure 2.6).
Imogene King (1923-2007) views the person as the patient in the nurse-patient relationship. Internal and external environments both generate stressors. Health is defined as the patient’s ability to function in societal roles. The focus of nursing is to help the patient maintain health so the patient can perform the duties related to the patient’s current role (King, 1981). For example, to ensure that an elderly patient who lives alone and has no transportation can receive hemodialysis three days a week, it would be necessary to incorporate the family in discharge planning.
Figure 2.6
Imogene King’s Theory of Goal Attainment
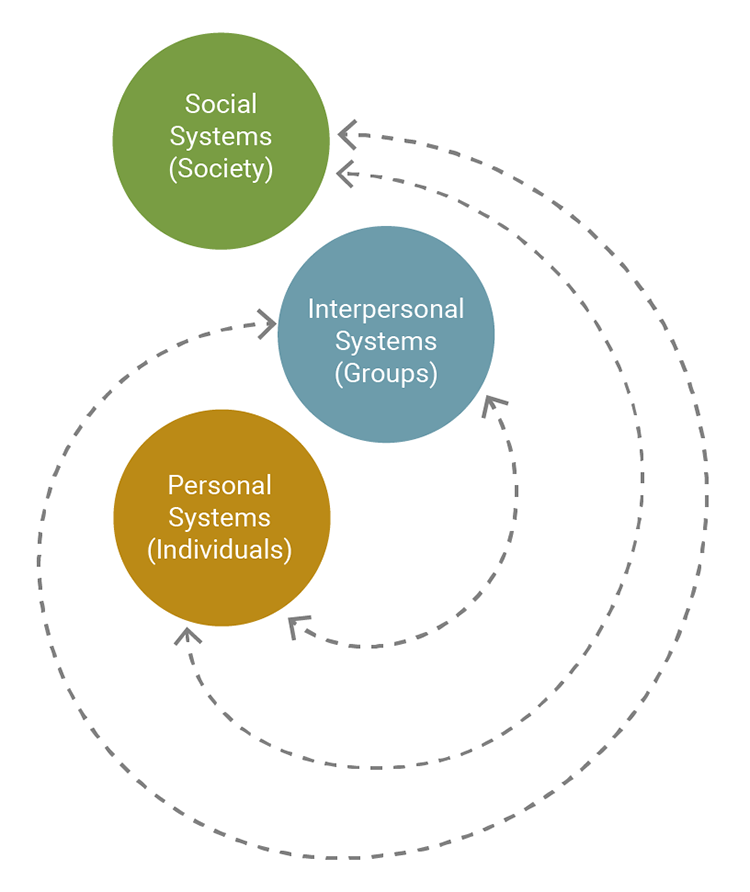
Note. Adapted from A Theory for Nursing: Systems, Concepts, Process, by I. M. King, 1981, p. 145.
Madeleine Leininger’s Cultural Care Theory
In Madeleine Leininger’s cultural care theory, she believed that cultural competency improved nursing practice. Madeleine Leininger’s (1925-2012) cultural care theory (see Figure 2.7) focuses on the analysis of different cultures to better understand their ideas of health, their behaviors, and their thoughts regarding nursing care (Creasia & Friberg, 2011).
The metaparadigm concept of Person is prominent in this theory, with its focus on better understanding of people and their cultural differences. Persons are not only referred to as human beings, but families, groups, and communities that contribute to their cultural background. The environment is where the individuals live, and it has an impact on a person’s ability to perform self-care. Leininger defined health as “a state of wellbeing that is culturally defined, valued, and practiced, and which reflects the ability of individuals (or groups) to perform their daily role activities in culturally expressed, beneficial, and patterned lifeways” (Leininger, 1991, p. 48). The goal of nursing is to support individuals to maintain or improve their health in a culturally competent way. An example of providing culturally competent care would be respecting the belief of a severely anemic patient who refuses blood products based on the patient’s religion as a Jehovah’s Witness.
Figure 2.7
Madeleine Leininger’s Cultural Care Theory
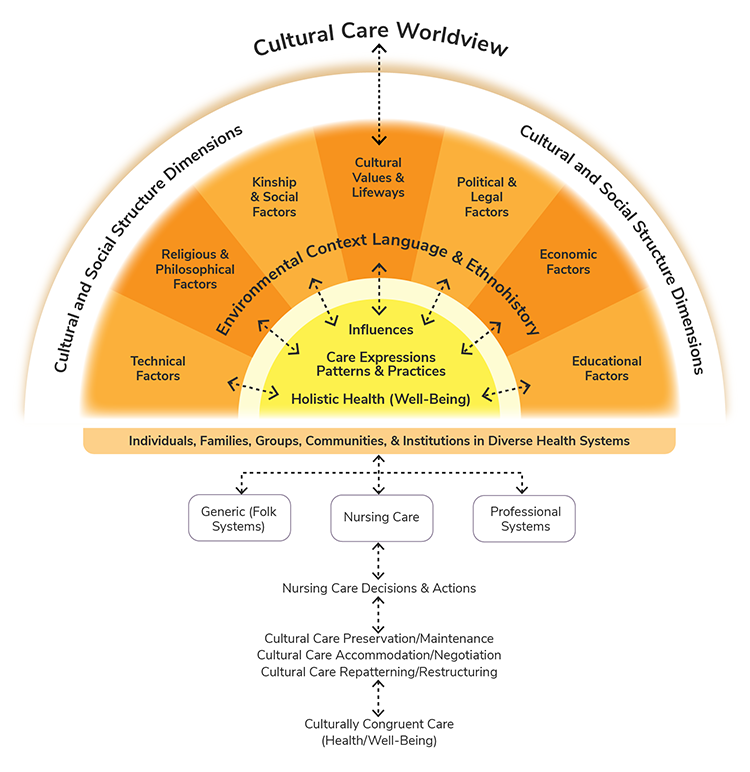
Note. Adapted from “The Sunrise Model: A Contribution to the Teaching of Nursing Consultation in Collective Health,” by L. Pereira de Melo, 2013, in American Journal of Nursing Research, 1(1), 20-23. Copyright 2013 by the Science and Education Publishing.
Midrange Theory Metaparadigm Concepts
Table 2.1 compares the midrange theories of Peplau, King, and Leininger and presents the midrange theoretical principals related to the metaparadigm concepts of nursing for deeper understanding.
Table 2.1
Midrange Theory Metaparadigm Concepts
Midrange Theorist
Person
Environment
Health
Nursing
Hildegard Peplau: Interpersonal Relations Theory
Viewed humans as organisms
Existing forces outside of the individual
Forward movement of human process toward creative and productive community living
Therapeutic interpersonal process
Imogene King: Theory of Goal Attainment
Patient in a nurse-patient relationship
Internal and external environments generate stress
Patient’s ability to function in current role
Assist the patient in maintaining health
Madeleine Leininger: Cultural Care Theory
Human beings, families, groups, communities
Where individuals live impacts ability for self-care
State of culturally defined well-being
Provide culturally competent support
Note. (Creasia & Friberg 2011; King, 1981; Leininger, 1991; Peplau, 1952)
Grand Theory
Lewin stated that exploring a variety of nursing theories could provide the nurse with new insights into patient care. The term grand theory indicates that the theory has a broad scope, including general concepts. The nature, purpose, and goals are broad (McEwen, 2007). Sister Callista Roy developed a grand theory in 1976 that is considered to be an adaptation model focusing on the human response and adaptation to a constantly changing environment. Grand theories typically are complicated and abstract and are not easily understood (Kolcaba, 2001).
Nightingale’s Environmental Theory
Florence Nightingale’s environmental theory presents disease as a reversible process achieved by altering the patient’s environment. Nightingale believed that individuals are in control of their own lives and desire good health. Also, the individual should be viewed as a holistic, multidimensional being, composed of biological, psychological, and spiritual components who possesses the ability to recover from disease if the environment allows. The environment is the most crucial concept in this theory (see Figure 2.8). Poor environmental factors lead to sickness and disease. Environmental factors include fresh air, sunlight, clean water, adequate food supply, efficient drainage, good hygiene, low noise, adequate temperature, and a clean environment. The environment is external; however, it can affect the individual in sickness or health. Nursing is a service intended to relieve pain and suffering.
It is the professional nurse’s responsibility to alter the patients’ environment to affect change in their health. The goal of nursing should be to promote the reparative process by manipulating the environment. Environmental change is needed for optimal health (Zborowsky, 2014).
Figure 2.8
Florence Nightingale’s Environmental Theory
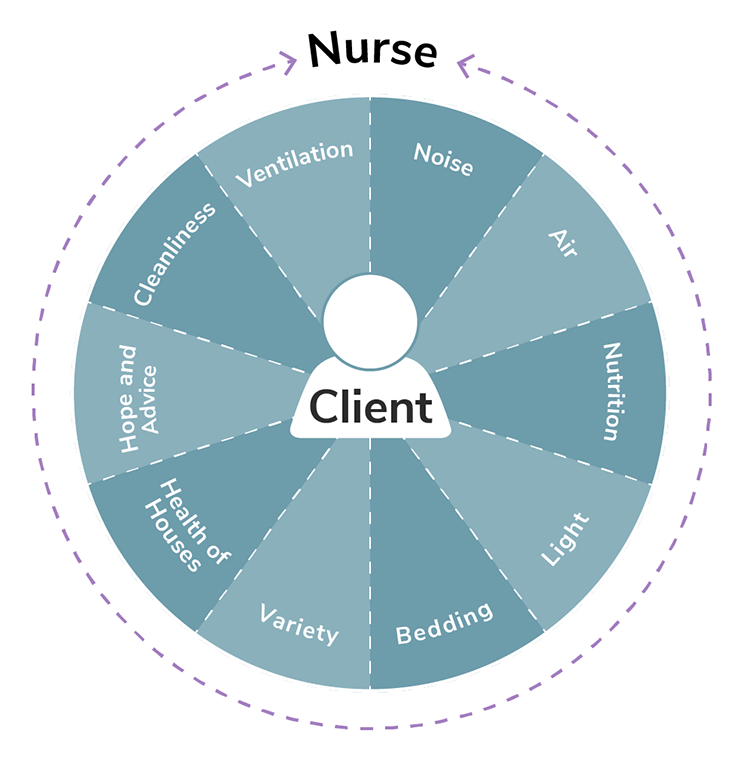
Note. Adapted from “Nightingale’s Environmental Theory Conceptual Framework,” by Nurselabs.com, 2014.
Rogers’s Science of Unitary Human Beings Theory
Martha Rogers’s science of unitary human beings theory was first publicized in 1970 in her publication, An Introduction to the Theoretical Basic for Nursing. She claimed that nursing was a science and an art. Her work began in the 1960s when she theorized that humans are dynamic energy fields that react with the environment and are continually changing. She viewed the individual as a whole energy field constantly in motion, with language and thought that are sensitive and emotional (see Figure 2.9).
Health is valued and occurs when living in harmony with the environment (Rogers, 1970).
Figure 2.9
Martha Rogers’s Science of Unitary Human Beings Theory
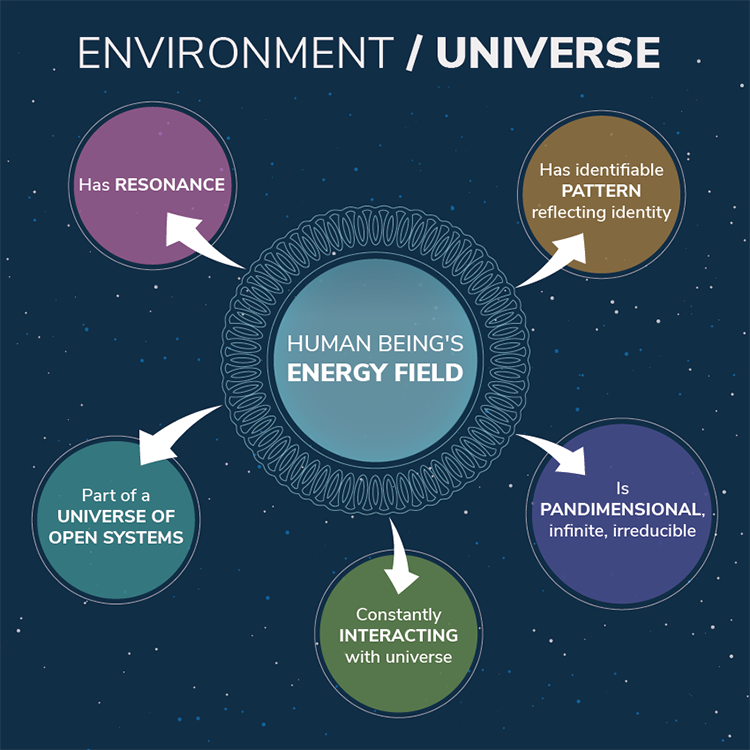 Example of Science of Unitary Human Beings TheoryA pediatric patient is hospitalized over the Christmas holiday. The patient’s mother, father, and two younger siblings are in the room as the nurse enters to assess the patient. The nurse feels that the atmosphere is very somber and wants to do something to improve the energy in the room. She mentions that she would be glad to bring in some Christmas DVDs if they are interested in watching movies. They agree, and when she enters the room an hour later, the family is laughing, enjoying a movie. The energy has changed in the room, and it feels more positive and cheerful.
Example of Science of Unitary Human Beings TheoryA pediatric patient is hospitalized over the Christmas holiday. The patient’s mother, father, and two younger siblings are in the room as the nurse enters to assess the patient. The nurse feels that the atmosphere is very somber and wants to do something to improve the energy in the room. She mentions that she would be glad to bring in some Christmas DVDs if they are interested in watching movies. They agree, and when she enters the room an hour later, the family is laughing, enjoying a movie. The energy has changed in the room, and it feels more positive and cheerful.
Orem’s Self-Care Deficit Theory
Dorothea Orem’s self-care deficit theory, developed during the years of 1959-2001, focuses on assisting others in managing self-care to maintain or improve human function at an effective level (Orem, 1995). Orem’s three-part theory includes self-care, self-care deficit, and nursing systems (see Figure 2.10).
Self-care is ideally performed by individuals to maintain health and well-being. Self-care deficit requires nursing assistance. Nursing systems define how the nurse will meet the individual’s needs. Orem’s theory states that the individual should be in an appropriate environment to receive care. The environment is external; however, for Orem’s theory, the environment and individual are bound together, and they function as one unit. Individual health is a condition in which humans are structurally and functionally complete. Health is considered physical, psychological, interpersonal, and social (Orem, 1995). The nursing focus should be to maintain health or to return the individual to the previous state of health by assisting with self-care to sustain life and maintain health (Current Nursing, 2012).
Figure 2.10
Orem’s Self-Care Deficit Theory
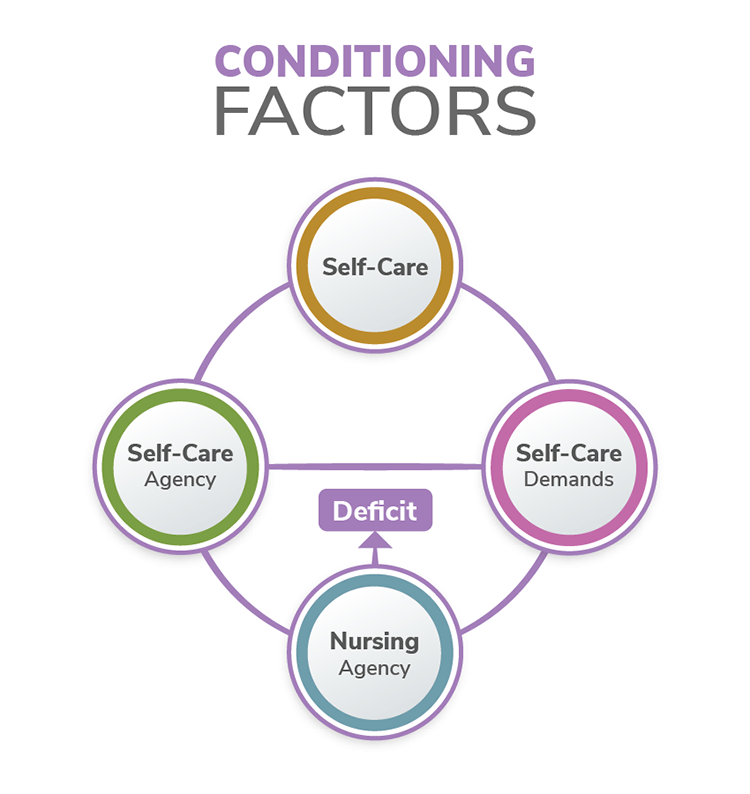
Grand Theory Metaparadigm Concepts
Table 2.2 compares the grand theories of Nightingale, Rogers, and Orem and presents the grand theoretical principals related to the metaparadigm concepts of nursing (person, environment, health, and nursing) for deeper understanding.
Table 2.2
Grand Theory Metaparadigm Concepts
Grand Theorist
Person
Environment
Health
Nursing
Nightingale: Environmental Theory
- Holistic and multidimensional
- Can recover from disease if environment allows
Poor environment leads to sickness and disease.
Goal is optimal health.
Responsibility to alter the patient’s environment
Rogers: Science of Unitary Human Beings
- Whole
- Not reducible
- Energy field
- Synergistic human beings
- Constantly reacting
- Exchanging matter and energy with humans
- Valued
- Occurs when living in harmony with environment
- Accepting of change
Viewed as a science and an art
Orem: Self-Care Deficit Theory
Individuals perform self-care to maintain health and well-being
External environment and individual bound together
Health is viewed as structurally and functionally complete
- Assist with self-care
- Help maintain or return to previous state of health
Note. (Orem, 1995; Rogers, 1970; Zborowsky, 2014; Current Nursing, 2012).
Future of Nursing
It is estimated that the future need of the nursing workforce will increase greatly in coming years. In fact, it is projected that the supply of professional nurses will increase from 3.5 million to 3.95 million by the year 2020; however, this supply will not meet the predicted demand, as more than 4.14 million nurses will be needed at that time. The increased need is partly because more than 70 million baby boomers will soon reach retirement age (Carnevale, Smith, & Gulish, 2015). The aging population will result in more elderly patients who are ill, seeking treatment, and requiring hospitalization and surgeries. Nursing shortages are commonplace across the United States. Nurses are leaving the profession because of retirement, inadequate wages, and stressful work environments related to insufficient staffing and long work hours. Hiring and retaining professional nurses is challenging for many employers. Although there has been an increase in students interested in entering the profession, nursing schools have had to turn students away because of a lack of faculty and facilities to educate them (Health Resources and Services Administration, 2017).
The IOM report, The Future of Nursing: Leading Change, Advancing Health (IOM, 2010), prioritizes the following areas of nursing: transforming practice, transforming education, and transforming leadership. The IOM report identifies several needs for the nursing workforce as it faces the complexity and challenges in today’s health care field. The future of nursing is changing and evolving. It is the duty of all nurses, from entry level to highly experienced, to embrace the changes and ensure that all patients are offered competent, safe, quality, compassionate care (IOM, 2010).
Reflective Summary
Professional nurses understand that nursing history defines the nurse’s role in current practice. Nursing’s rich history before Christianity, in the Middle Ages, during the 1700s, and through the 21st century have shaped the nursing profession. Many nurse leaders have contributed to this history, including pioneers such as Florence Nightingale, Lillian Wald, Clara Barton, and Linda Richards, who have paved the way for future generations of nurses.
Nursing is a knowledge-based discipline and profession that incorporates a body of knowledge to guide its practice (Smith & Parker, 2015). Through the years, professional nurses have identified theories that attempt to explain relationships between nursing care and the patient. These theories are categorized according to their complexity and can be referred to as practice theories, midrange theories, and grand theories or conceptual models. The scope and status of nursing education have dramatically changed from the days of nurse training programs in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Many nursing education delivery models have evolved. Today, nurses can earn degrees at several levels, with several delivery methods available. The IOM report, The Future of Nursing: Leading Change, Advancing Health (IOM, 2010), emphasizes the transformation of practice, education, and leadership as priorities that will allow the nursing profession to continue to evolve through the 21st century and beyond.